What Is Tendinopathy Of The Posterior Tibialis Muscle?
Tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle, also known as flatfoot, is a condition that affects the posterior tibial tendon and has a rather good prognosis when treated early.
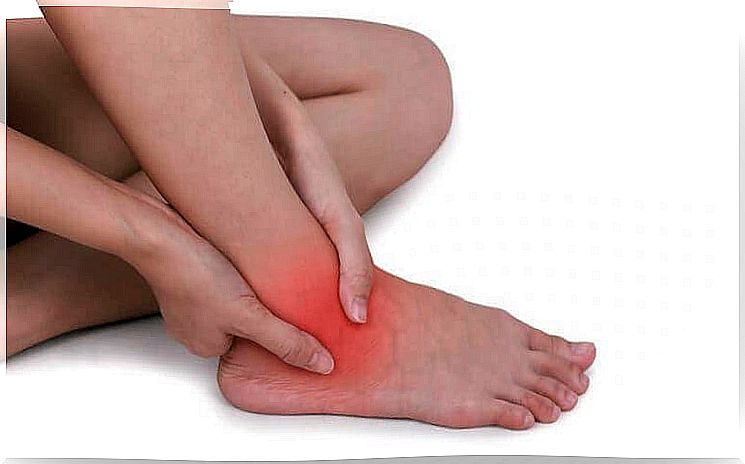
Posterior tibialis tendinopathy is an injury to the tendon, which causes pain, swelling and limits movement. The tendon affected in this pathology is that of the posterior tibialis muscle, fundamental in the functions of the ankle and the foot.
The posterior tibialis muscle is an elongated muscle in the leg, which is located in the calf. The insertion of this muscle goes from the tibia, fibula and interosseous membrane (the one that connects the two bones) to the lower part.
This muscle continues on its way in the form of a tendon, passing behind the tibial malleolus, which is the inside of the ankle. It then fits into the scaphoid or navicular bone which is located at the top of the arch of the foot.
It also fits into the cuneiform bones and the three central metatarsals, the bones in the front of the foot. As you can see, the muscle and tendon occupy a large part of the ankle and the foot, and therefore are crucial in its function.
What is tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle?
As we have already pointed out, tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle is a lesion of the homonymous tendon.
The word tendinopathy is a general term used to refer to both tendonitis and tendinosis. So, when we talk about tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle, we are referring to these two types of lesions.
Tendinitis involves inflammation of the tendon, while tendinosis refers to a degenerative process of the tendon. However, many researchers believe that the term tendonitis is imprecise for this case and that the word tendinopathy should always be used instead.
Tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle causes severe limitations in the movement of the foot and ankle. Indeed, the posterior tibia performs important functions, namely:
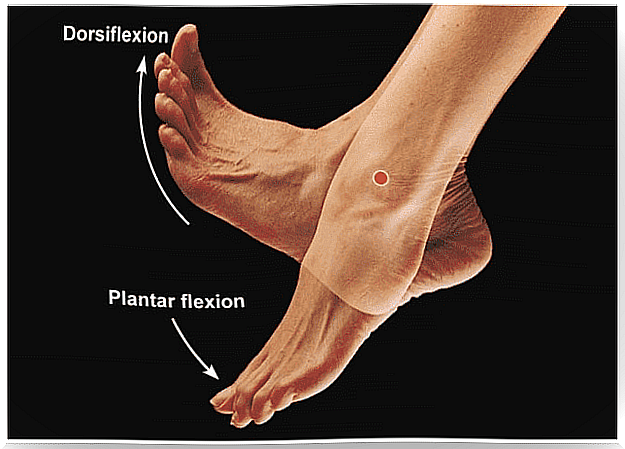
- Plantar flexion of the ankle. Movement in which the toe is lowered
- Ankle supination When the sole of the foot is pointed inward and upward.
- If the foot is resting on the ground, the posterior tibia slows down pronation and rotates the tibia inward, that is, to turn the leg inward.
Causes of tendinopathy
Posterior tibialis tendinopathy is an overuse injury that primarily affects runners and walkers. It is caused by anatomical and / or biomechanical factors.
Among the anatomical and biomechanical factors that cause tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle, excessive pronation can be distinguished. This is the normal inward rotation of the foot when walking. Very often, this excessive pronation is the consequence of flat feet. This puts undue stress on the tendon.
Another anatomical factor is being overweight, or high body mass index (BMI). It is also influenced by previous inflammatory diseases, neurological conditions or degenerative changes in the joints. Tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle is more common in women over 40 years of age.
With regard to bad practices and the use of materials, the main causes are: the use of unsuitable footwear, excessive walking and poor walking or running technique. Muscle weakness and inflexibility in the ankle muscles may also play a role.
Characteristics and other data of interest
The course of tendinopathy of the posterior tibialis muscle passes through four phases, each of which has characteristic symptoms. Here they are :
- Phase I: presence of pain inside the ankle, during the inversion movement of the foot and on palpation of the tendon. There is also inflammation around the ankle
- Stage II: The above symptoms persist and are made worse by difficulty staying on tip-toe and “lame foot”. The arch of the foot appears flattened
- Phase III: to the symptoms of the previous phases is added the deformation of the foot, which is now flat. There are also degenerative changes in the subtalar joint
- Stage IV: in addition to all of the above, there is degeneration of the pereno-talar joint
Posterior tibialis tendinopathy, like other tendinopathies, can even lead to tendon rupture. Early treatment and reversing the underlying cause dramatically improves the prognosis of this disease. In more severe cases, surgery is required.